Your genes and exercise
posted 17th February 2025
Your genes and exercise
- Exercise is not only good for our physical health, but it benefits our mental health and abilities too.
- Physical exercise can affect how much of certain proteins are made in the brain.
- Physical exercise produces many benefits in the brain that enhance cognitive function, blood flow and resistance to injury.
- One mechanism to account for the changes in brain plasticity is through the action of growth factors
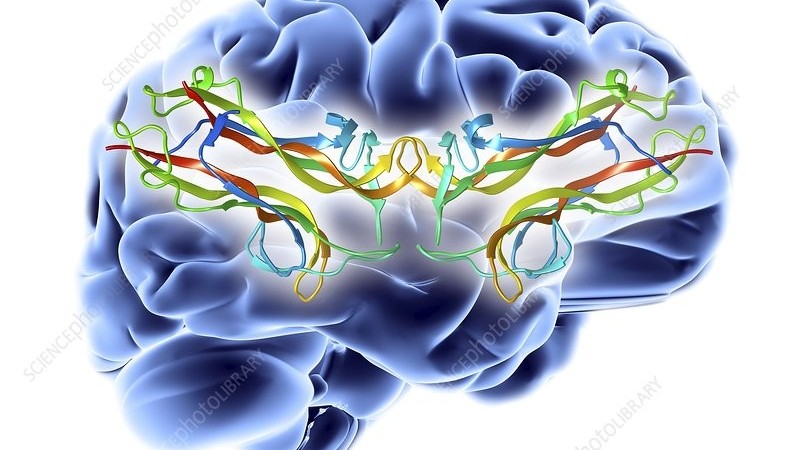
- In particular, the levels of a protein called brain derived neurotrophic factor (or BDNF for short) increase after exercise.
- BDNF is a protein involved in neuronal development and neural plasticity.
- A major contributor to the processes of learning and memory formation BDNF signaling pathways.
- It has been known for over two decades that physical activity or neuronal activity markedly enhances BDNF gene expression in the brain and that this increase in BDNF protein leads to activation of signaling pathways that result in exercise-dependent enhanced learning and memory formation.
- BDNF has already been shown to enhance mental abilities at the same time as acting against anxiety and depression in mice and might act in similar way in humans.
- Engagement in regular bouts of exercise confers numerous positive effects on brain health across the lifespan.
- Exercise induces changes in class I HDAC expression and binding to the hippocampal BDNF promoter
- Acute bouts of exercise transiently improve cognitive function, while long-term exercise training stimulates brain plasticity, improves brain function, and helps to stave off neurological disease.
- The action of BDNF is a candidate mechanism underlying these exercise-induced benefits and is the subject of considerable attention in the exercise-brain health literature.
- It is well established that acute exercise increases circulating levels of BDNF, and numerous studies have sought to characterize this response for the purpose of improving brain health.
- Exercise promotes the expression of BDNF through the action of the ketone body β-hydroxybutyrate.
- Exercise induces beneficial responses in the brain, which is accompanied by an increase in BDNF, a trophic factor associated with cognitive improvement and the alleviation of depression and anxiety.
- Studies have shown that Met/Met carriers of European descent with depression may have a poor response SSRI's and improved response to Duloxetine, Venlafaxine and Clomipramine; further studies need to confirm these findings.
- Exercise has been linked to improvement in cognition and stress response with Met carriers showing a more pronounced response.
- Patients with the Met/Met gene variation usually show altered BDNF secretion and the clinical impact suggests that increased levels of physical activity and exercise and supplementation with omega-3 can improve cognition and the stress response.
If you would like to find out more about genetic testing, then please GetInTouch

